Bioinformatics Tools
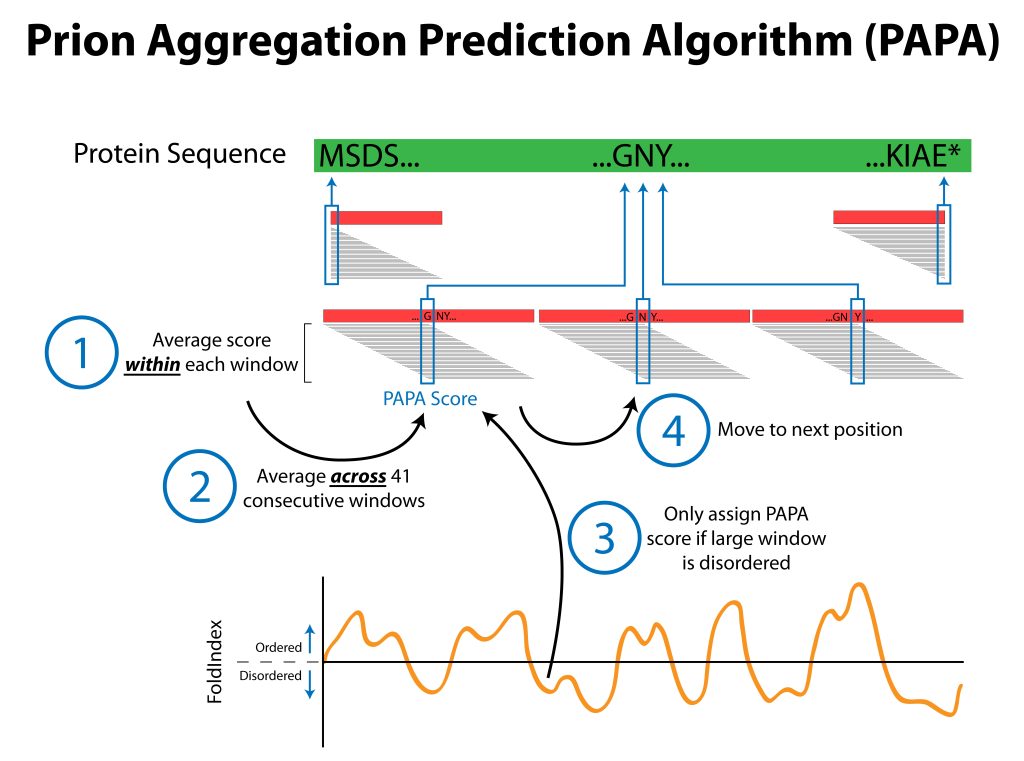
Prion Aggregation Prediction Algorithm (PAPA)
Prions are infectious proteins. PAPA is a tool our lab developed to predict prion activity from a protein’s amino acid sequence. A prion propensity score was determined experimentally for each of the 20 canonical amino acids. These scores are then used to predict the prion propensity of a protein of interest using a sliding window and a series of averages within and across windows. In addition, known prion domains are often intrinsically disordered: therefore, PAPA preferentially scores regions that are predicted to be disordered. The original PAPA source code and webserver can be found here, and you can read more about PAPA here. A more recent version of PAPA (called mPAPA) can be found here, and you can read more about mPAPA here. In addition to identifying the highest-scoring window, mPAPA merges overlapping windows and can help users identify the largest domains scored as prion domains.
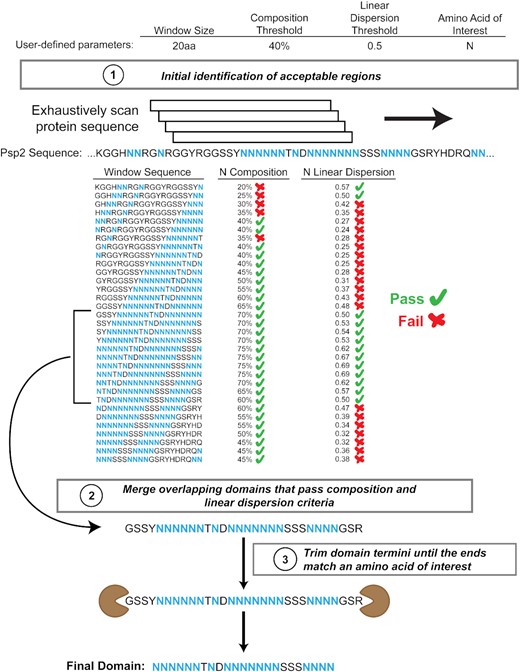
Low-Complexity Domain Composition Scanner ("LCD-Composer")
Low-complexity domains “LCDs” are regions in protein sequences that are enriched in one or a few amino acids. LCDs are involved in a variety for normal and pathological processes, including cellular stress responses, endocytosis, neurodegenerative disorders, and cancer. LCD-Composer is a tool to identify LCDs based on user-specified minimum composition criteria. LCD-Composer is extremely flexible, allowing users to specify any combination of amino acids and any minimum enrichment threshold. The LCD-Composer webserver can be found here, and you can read more about LCD-Composer here and here. To run large-scale analyses using LCD-Composer, you can also download our open-source scripts here.
Image taken from Cascarina et al. (2021) NAR Genom and Bioinform.
